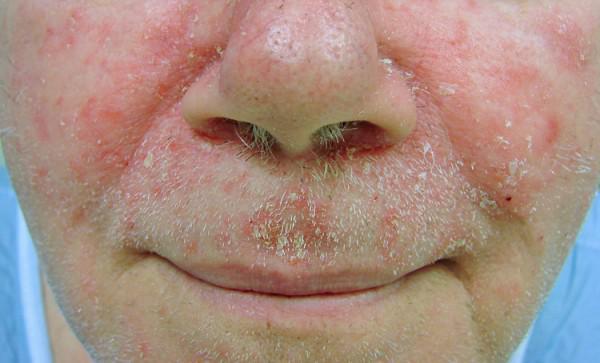
What is seborrheic dermatitis? Seborrheic dermatitis is a very common skin disease that causes a rash. When this rash appears the skin tends to have three main characteristics:
- Reddish color
- Swollen and greasy appearance
- White and/or yellowish crusty scale on the surface
Sometimes, more than one of the rashes listed above can be present on the body. These rashes can sometimes itch, but not always. There is still much research being done to find out more about what causes this skin disease. We currently know that many factors play a part in causing it. Such factors include the yeast that normally lives on our skin, our genetics, living in cold and dry climates, stress, and a person’s overall health. Other than irritation (burning and itching in affected areas), this disease is not harmful to the body. This disease is not caused by poor hygiene and it is not an allergic reaction to a foreign substance. We do know that people of all colors and ages get seborrheic dermatitis. The age groups that are most susceptible are infants 3 months of age or younger, and adults between ages 30 and 60 years of age.
The Disease in Infants:
If you have ever heard of an infant getting “Cradle Cap”, this is referring to seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp of the infant. Many infants can get this disease. Scaly, greasy patches will form on the baby’s scalp, and the patches can become thick and crusty. If you have an infant that exhibits this kind of rash, do not fret, as this form of seborrheic dermatitis is harmless. The rash can go away on its own within a few months. If you would like for your child to receive treatment, however, Pine Belt Dermatology can certainly help. The scalp isn’t the only area that an infant can get this disease. Babies can also get seborrheic dermatitis in their diaper area and elsewhere. In the diaper area, the red rash is often mistake as diaper rash. Seldom, babies will get seborrheic dermatitis that covers much of the body with red and scaly patches. If this is the case feel free to schedule an appointment with a Pine Belt dermatology provider. No matter where the seborrheic dermatitis forms on your baby, it tends to permanently disappear between 6 months and 1 year of age. Seborrheic dermatitis varies in how it is presented based on a patient’s age. Signs and symptoms of the disease in babies include:
- Yellow greasy scale on the scalp
- A thick layer of scale can cover the entire scalp
- Scale will present itself as yellow or brownish color
- In time, scale will flake and rub off of the scalp.
So how do we treat it for infants? Shampooing the scalp daily with a baby shampoo can help. Gently brushing away the scale once it starts to soften will help. You can also apply medications to the infant’s scalp to help expedite the healing process.
Seborrheic Dermatitis in Adults:
When this disease presents itself in adults, the condition can come and go for the rest of that person’s life. Flare-ups are common when the weather turns cold and dry, similar struggles for people with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. The good news is that treatments can reduce flare ups and bring relief to the affected areas. The disease affects adolescents and adults differently than it does in infants. In older patients the disease causes:
- Scaly patches on the skin
- Skin beneath these patches ae reddish
- Even though scale is present, patches often look greasy or moist
- Scale will flake off and look yellowish, sometimes white.
- Itching of the skin, especially in the ear canal and on the patient’s scalp.
- Affected area can sometimes exhibit a burning sensation
Seborrheic dermatitis causes patches to form where the skin is oily, such as:
- Scalp
- Ears, especially the ear canal
- Eyebrows
- Center of the face
- Eyelids
- Upper chest and back
- Armpits
- Genitals
As mentioned above, seborrheic dermatitis can affect all ages and all ethnicities and there are some medical conditions that can increase your risk of exhibiting the disease. Those medical conditions include, but are not limited to:
- HIV – roughly 85% of people infected with HIV develop seborrheic dermatitis
- Acne
- Rosacea
- Psoriasis
- Epilepsy
- Parkinson’s disease
- Recovering from a stroke or heart attack
- Eating Disorder
- Alcoholism
- Depression
After infancy, seborrheic dermatitis usually does not go away in adolescents and adults without treatment. There are a few different treatment options at our disposal to treat the disease. Treatments include: dandruff shampoos, medicine to apply to the skin for short periods of time, and barrier-repair creams. Dandruff shampoos can be helpful on the skin as well as the scalp. Often the best results come from combining two or more treatments, and this combination will be determined when you consult one of our providers.
The good news is that seborrheic dermatitis is a disease that Pine Belt Dermatology & Skin Cancer Center frequently diagnoses and treats. If you suspect you have seborrheic dermatitis, you should schedule a visit with myself or one of my colleagues for a diagnosis. While the disease is harmless, it does cause irritation, and it is important to make sure we rule out other diseases. Diseases that can be confused with seborrheic dermatitis include psoriasis, eczema, or an allergic reaction of the skin. Each of these diseases requires different treatments. Although treatment cannot cure seborrheic dermatitis, treatment has benefits. Treatment can loosen and remove scale, prevent a skin infection, and reduce swelling and itch. However, to get the proper treatment it is important that you schedule a visit with a provider. The right treatment requires the right diagnosis!