Beyond Acne: Understanding and Treating Adult Skin Conditions
Beyond Acne: Understanding and Treating Adult Skin Conditions
While acne is often associated with teenagers, adults are not immune to skin conditions that affect their confidence and overall well-being. Beyond acne, a wide range of dermatological issues can emerge due to aging, environmental exposure, genetics, or underlying health conditions. Understanding these conditions, their causes, and available treatments is essential for maintaining healthy skin.
Let’s explore common adult skin conditions, their symptoms, potential causes, and effective treatment options.
Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that leads to redness, dryness, and intense itching. It can occur at any age but is often seen in adults who have a history of allergies or asthma.
Causes of Eczema
It is thought that both environmental and genetic factors contribute to eczema. The condition is more common in people who have a family history of hay fever, asthma, or eczema. Environmental triggers such as allergens, pollutants, harsh chemicals, and extreme weather conditions can worsen symptoms. Stress and hormonal changes may also play a role in flare-ups.
Common Symptoms
Eczema manifests as dry, red, and itchy skin that can become cracked or inflamed. In severe cases, the affected areas may weep or develop scabs. The itching can be intense, often leading to excessive scratching that further damages the skin barrier, increasing the risk of infections. The condition commonly appears on the hands, elbows, knees, and face, though it can affect any part of the body.
Treatment Options
Managing eczema involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Moisturizing regularly with hypoallergenic creams helps restore the skin barrier and prevent dryness. Prescription-strength corticosteroids or immunomodulators can reduce inflammation, while antihistamines may help control itching. In some cases, biologic medications may be recommended for severe eczema. Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as fragrances or extreme temperatures, is crucial for long-term management. Maintaining a skincare routine with gentle, fragrance-free products can also help minimize flare-ups.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin disorder characterized by persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and acne-like bumps, particularly on the face.
Causes of Rosacea
The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Triggers such as sun exposure, spicy foods, alcohol, hot beverages, and stress can lead to flare-ups. An overactive immune response and the presence of certain skin mites (Demodex) have also been linked to the condition.
Common Symptoms
Rosacea often presents as facial redness, swollen blood vessels, and small, red, pus-filled bumps. Some individuals experience eye irritation, dryness, or a burning sensation. In more severe cases, the nose may become thickened and bulbous, a condition known as rhinophyma.
Treatment Options
Dermatologists often recommend topical treatments like metronidazole or azelaic acid to reduce redness and inflammation. Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline may be prescribed for severe cases. Laser therapy is an effective option for reducing visible blood vessels. Patients are advised to use gentle skincare products, apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, and avoid known triggers.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that accelerates the skin cell turnover process, leading to scaly, inflamed patches, often on the elbows, knees, and scalp.
Causes of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is linked to an overactive immune system that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with many affected individuals having a family history of the condition. Triggers such as stress, infections, cold weather, and certain medications can lead to flare-ups.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of psoriasis include thick, red areas that are covered in silvery scales. The affected skin may be itchy, painful, or prone to cracking and bleeding. Some individuals develop nail changes or joint pain, a condition known as psoriatic arthritis.
Treatment Options
Mild cases can be managed with topical corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs like calcipotriene. For moderate to severe cases, systemic treatments such as biologic drugs (e.g., adalimumab, secukinumab) that target immune responses are often used. Phototherapy, which involves controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, can also help reduce symptoms.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of certain areas of the skin due to excessive melanin production.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by sun exposure, hormonal changes (such as melasma during pregnancy), inflammation from acne, or skin injuries. Certain medications and medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease, can also contribute to the condition.
Common Symptoms
Dark patches or spots appear on the skin, commonly on the face, hands, and other sun-exposed areas. The discoloration may range from light brown to deep black, depending on skin tone and severity.
Treatment Options
Topical treatments containing hydroquinone, kojic acid, or vitamin C can lighten dark spots over time. Chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and laser therapy are effective in promoting skin renewal and reducing pigmentation. Daily sun protection is crucial to prevent further discoloration.
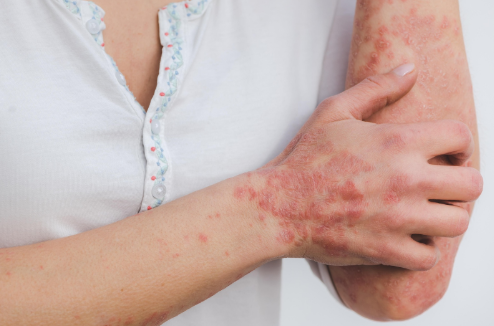
Hives
Hives (urticaria) appear as raised, itchy welts on the skin and can result from allergic reactions to foods, medications, insect bites, or even stress. Chronic urticaria, lasting longer than six weeks, may indicate an underlying autoimmune disorder.
Causes of Hives
Hives occur when the body releases histamines in response to allergens, stress, or infections. Certain medications, food additives, extreme temperatures, and insect stings can also trigger outbreaks. In chronic cases, autoimmune disorders may play a role.
Common Symptoms
Hives present as red or skin-colored welts that can vary in size and shape. They may appear suddenly and move around the body, often causing itching or a burning sensation. In severe cases, swelling of the lips, eyelids, or throat (angioedema) may occur.
Treatment Options
Antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine, are commonly used to manage symptoms. For severe cases, corticosteroids or biologic drugs like omalizumab may be prescribed. Identifying and avoiding potential allergens is key to preventing recurrences. In cases of life-threatening allergic reactions, epinephrine injections may be necessary.
Skin Cancer
Skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, is one of the most serious adult skin conditions. Prolonged sun exposure, tanning beds, and genetic factors increase the risk.
Causes of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer develops when DNA damage from ultraviolet (UV) radiation or other carcinogens leads to uncontrolled cell growth. Risk factors include prolonged sun exposure, fair skin, weakened immune function, and family history of skin cancer.
Common Symptoms
The most common signs include changes in moles, new growths, or non-healing sores. Basal cell carcinoma often appears as a pearly bump, while squamous cell carcinoma may present as a scaly, red patch. Melanoma is the most aggressive type, characterized by asymmetrical, dark, or irregularly bordered moles.
Treatment Options
Early detection is critical for effective treatment. Surgical removal, cryotherapy, or Mohs surgery are common treatment methods. Advanced cases may require radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. Regular skin checks and consistent use of sunscreen are essential preventive measures.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to an irritant or allergen, leading to redness, itching, and blistering. Common triggers include soaps, fragrances, cosmetics, and certain metals like nickel.
Causes of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is triggered by direct skin exposure to irritants (e.g., detergents, solvents) or allergens (e.g., latex, poison ivy). Individuals with sensitive skin or a history of allergies are more susceptible.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms include redness, itching, swelling, and blistering of the affected area. In severe cases, the skin may crack, ooze, or become thickened from repeated exposure.
Treatment Options
Avoiding the offending substance is the primary solution. Over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams and antihistamines can relieve mild symptoms. Severe cases may require prescription corticosteroids. Patch testing by a dermatologist can help identify specific allergens.
Perioral Dermatitis
Perioral dermatitis manifests as red, bumpy rashes around the mouth and nose. It is often linked to overuse of topical steroids, hormonal changes, or certain skincare products.
Causes of Perioral Dermatitis
Triggers include prolonged use of topical steroids, excessive use of heavy skincare products, hormonal fluctuations, and bacterial or fungal infections.
Common Symptoms
The condition presents as clusters of red, inflamed papules around the mouth, nose, and occasionally the eyes. The rash may cause burning or mild itching.
Treatment Options
Discontinuing topical steroids and using mild, fragrance-free cleansers can improve symptoms. Dermatologists may prescribe oral antibiotics like tetracycline or topical treatments like metronidazole.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis leads to flaky, itchy skin, primarily on the scalp, face, and chest. It is associated with yeast overgrowth and excess oil production.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis
This condition is linked to an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, excessive oil production, and genetic predisposition. Cold, dry weather and stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Common Symptoms
Seborrheic dermatitis causes yellowish, greasy scales on the scalp, eyebrows, sides of the nose, and behind the ears. Itching and redness are common, and in severe cases, the skin may crack or become inflamed.
Treatment Options
Antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide are effective in managing symptoms. Topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors can help reduce inflammation. Regular washing with mild cleansers can prevent flare-ups.
Preventative Measures for Healthy Skin
Taking proactive steps can help prevent and manage many adult skin conditions:
- Sun Protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) daily to prevent UV damage and hyperpigmentation.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Drinking plenty of water and consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins supports skin health.
- Gentle Skincare Routine: Avoid harsh products that strip the skin. Opt for fragrance-free, non-comedogenic cleansers and moisturizers.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate skin conditions. Practices like yoga, meditation, and adequate sleep can help.
- Regular Dermatologist Visits: Routine skin checkups help detect issues early, allowing for prompt treatment.
If you're struggling with persistent skin conditions beyond acne, our expert dermatologists at
Pine Belt Dermatology are here to help. We provide personalized treatment plans tailored to your unique skin needs, whether you're dealing with eczema, rosacea, psoriasis, or other chronic concerns.
Book your appointment with us today and take the first step toward healthier, clearer skin.