A Comprehensive Guide on Understanding and Managing Yeast Infections on the Skin
A Comprehensive Guide on Understanding and Managing Yeast Infections on the Skin

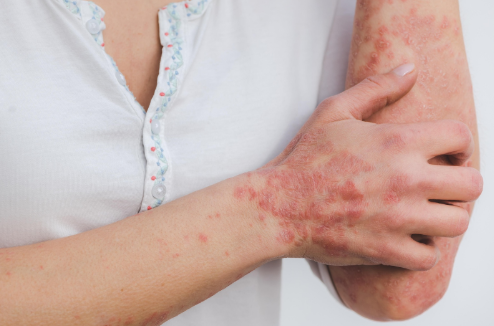
Yeast infections on the skin can be uncomfortable and persistent if not properly managed. Medically known as cutaneous candidiasis, a yeast infection on the skin arises when a fungus called Candida albicans overstays its welcome. While a small amount of Candida naturally lives on our skin, an imbalance can lead to an itchy, red, and uncomfortable rash.
Keep reading to learn the causes, symptoms, treatments, and when to seek medical attention for yeast infections on the skin.
Understanding Yeast Infections on the Skin
Yeast, a fungus, naturally inhabits the skin and resides in the digestive system. However, an overgrowth of yeast on the skin or other regions can lead to an infection. This infection is also called candidiasis. Understanding the dynamics of yeast infections on the skin is essential for recognizing symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and implementing preventive measures to maintain skin health and overall well-being.
Causes of Yeast Infections on the Skin
Yeast infections on the skin develop when there is an imbalance in the microbial flora, allowing Candida yeast to proliferate. Several factors contribute to the development of yeast infections on the skin:
Candida Albicans Overgrowth
Candida albicans is a fungus that thrives in warm, moist environments. It makes areas of the skin with skin folds, such as the groin, armpits, and beneath the breasts, particularly susceptible to infection. When conditions favor its growth, such as prolonged moisture or compromised skin integrity, Candida albicans can multiply rapidly, developing a yeast infection.
Warm and Moist Environments
Yeast infections on the skin often flourish in warm and moist environments, creating an ideal breeding ground for fungal growth. Sweat-inducing activities, like exercise or wearing tight clothing for an extended period, can create ideal conditions for yeast growth. Additionally, humid climates or excessive moisture from swimming or bathing without proper drying can exacerbate the risk of developing a yeast infection.
Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system can compromise the body's ability to ward off infections, including yeast infections on the skin. Individuals with conditions such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders are particularly susceptible to fungal infections due to their impaired immune response. Moreover, certain medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, can further weaken the immune system, increasing the likelihood of yeast infections.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain underlying health conditions can predispose individuals to yeast infections on the skin. Diabetes, in particular, poses a significant risk due to elevated blood sugar levels that promote yeast overgrowth. Pregnant women are also prone to yeast infections, as hormonal changes can alter the skin's pH balance and mucous membranes, creating an environment conducive to fungal growth. Moreover, individuals with a history of recurrent yeast infections may have an underlying medical condition that requires further evaluation and management.
Antibiotics and Other Medications
Antibiotics, while essential for treating bacterial infections, can disrupt the balance of microorganisms on the skin and mucous membranes. By targeting harmful bacteria, antibiotics may also eliminate beneficial bacteria that help regulate yeast growth. This allows for Candida albicans overgrowth and subsequent infection. Similarly, the prolonged use of corticosteroids or immunosuppressants can weaken the skin's natural defenses, increasing susceptibility to yeast infections.
Symptoms of Yeast Infections on the Skin
Yeast infections on the skin can present with a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. It is crucial to identify these symptoms to ensure a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Common symptoms include:
Redness and Inflammation
The skin may appear reddened, irritated, and swollen, indicating an inflammatory response to Candida albicans. This redness causes warmth and tenderness, particularly in skin folds and creases where moisture can accumulate.
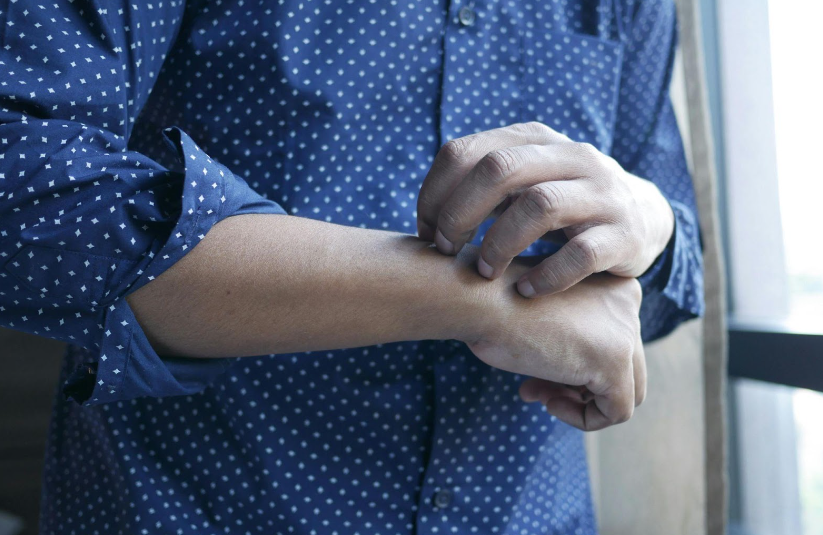
Itching and Irritation
Yeast infections on the skin commonly cause intense itching and irritation, prompting individuals to scratch the affected area to alleviate discomfort. The itching may be persistent and disruptive, exacerbating skin inflammation and further damage. It is essential to avoid excessive scratching, as this can increase the risk of secondary bacterial infections and worsen symptoms.
Rash or Patches of Raised Skin
A characteristic feature of yeast infections on the skin is rashes or raised skin patches that may have a distinct border. These rash-like lesions can vary in size and distribution, appearing as tiny red bumps or larger, confluent areas of inflammation. The affected skin may develop a shiny or glazed appearance in some cases, indicating ongoing inflammation and moisture retention.
Soreness and Discomfort
Individuals with yeast infections on the skin often experience soreness and discomfort, especially in areas where friction and moisture exacerbate symptoms. Walking, sitting, or wearing tight clothing may exacerbate discomfort and worsen symptoms. Persistent soreness and discomfort should prompt individuals to seek medical evaluation for an appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
White or Yellow Discharge
Occasionally, yeast infections on the skin may produce a white or yellow discharge, particularly in warm and moist areas such as skin folds and sensitive areas. This discharge may have a thick, curd-like consistency and a foul odor. It is essential to note any changes in discharge and seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
Risk Factors for Yeast Infections on the Skin
Several factors increase the risk of developing yeast infections on the skin:
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase moisture and friction in skin folds, creating an ideal environment for yeast overgrowth.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more prone to yeast infections due to elevated blood sugar levels, which promote yeast growth.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of developing yeast infections on the skin.
- Immunosuppression: Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, and organ transplantation weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to yeast infections.
- Antibiotic Use: Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of microorganisms on the skin, leading to yeast overgrowth.
How Is Candidiasis of the Skin Diagnosed?
Your doctor will likely be able to diagnose you simply by performing a physical examination. Throughout the examination, they will observe the rash's location and assess the condition of your skin's appearance.
Your doctor may also want to perform a skin culture before diagnosing candidiasis of the skin.
In a skin culture procedure, your physician gently swipes a cotton swab across the affected area to gather a skin sample. Later, specific laboratory tests will confirm the presence of infection in the sample.
Treatment Options for Yeast Infections on the Skin
Treatment for yeast infections on the skin typically involves antifungal medications and lifestyle modifications to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Here are some effective treatment options:
Topical Antifungal Creams
Over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal creams containing active ingredients such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or ketoconazole can effectively treat yeast infections on the skin. You can apply these creams directly to the affected areas according to the instructions.
Antifungal Powders
Antifungal powders help keep the affected areas dry and prevent moisture buildup, which can promote yeast growth. Apply antifungal powders to skin folds and other susceptible areas to reduce friction and irritation.
Prescription Medications
In severe cases or when OTC treatments fail to provide relief, your healthcare provider may prescribe oral antifungal medications or stronger topical creams to combat the infection.
Maintain Good Hygiene
Good hygiene habits are essential for preventing and managing yeast infections on the skin. Keep the affected areas clean, dry, and well-ventilated, and avoid wearing tight-fitting clothing that can trap moisture.
Avoid Irritants
Avoid harsh soaps, perfumes, and skincare products that irritate the skin and exacerbate symptoms. Opt for gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers to soothe the skin.
When to See a Doctor
You can treat most yeast infections on the skin at home using OTC medications and self-care measures. However, it is essential to seek guidance from a doctor if:
Symptoms Persist or Worsen
If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
Recurrent Infections
Are you getting fungal infections frequently? Then it's high time to see a doctor. An underlying medical condition or risk factor may be at play when yeast infections recur on the skin.
Severe Symptoms
If you experience severe symptoms such as intense itching, pain, swelling, or signs of infection such as fever or pus-filled blisters, seek medical attention promptly.
Pregnancy or Nursing
Pregnant or nursing individuals should consult their healthcare provider before using any medications to treat yeast infections on the skin.
Immune System Disorders
Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, should seek medical advice for proper management of yeast infections on the skin.
Final Thoughts
Yeast infections on the skin can cause discomfort, irritation, and embarrassment, but with proper treatment and preventive measures, most cases can be effectively managed. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for yeast infections on the skin, you can take proactive steps to promote skin health and overall well-being. Remember to practice good hygiene, wear breathable clothing, and seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms. With the right approach, you can minimize the impact of yeast infections on your skin and enjoy healthier, happier skin.
At
Pine Belt Dermatology, our team of experienced dermatologists specializes in diagnosing and managing various skin conditions, including candidiasis. Our dermatologists have the expertise to diagnose and treat your skin yeast infection effectively. We offer personalized treatment plans and work closely with you to prevent future occurrences. If you're struggling with a persistent itch or suspect a yeast infection, don't hesitate to
schedule an appointment
with us. We're here to help you regain clear, comfortable skin and restore your confidence.


Petal Office
Phone:
Fax:
601-336-7826
Address:
Hours of Operation:
Mon-Fri: 8:00am to 4:30pm
Hattiesburg Office
Phone:
Fax:
601-475-9969
Address:
Hours of Operation:
Mon-Fri: 8:00am to 4:30pm
Ellisville Office
Biloxi Office
Phone:
Fax:
228-232-0874
Address:
1009 Tommy Munro Drive, Suite A
Hours of Operation:
Mon-Fri: 8:00am to 4:30pm
Ocean Springs Office
All Rights Reserved | Pine Belt Dermatology